 Lung is an organ with important functions: Here, the oxygen enters the blood and the blood flow to all body cells. Oxygen is required for basic metabolism. could he not have a job, the organism is no longer. Breath "" through the lungs occurs automatically, without thinking about the needs of people.
Lung is an organ with important functions: Here, the oxygen enters the blood and the blood flow to all body cells. Oxygen is required for basic metabolism. could he not have a job, the organism is no longer. Breath "" through the lungs occurs automatically, without thinking about the needs of people.Structure is how the parts of something related to each other or how something is put together. Structure is fundamental to any system properties. Identification of a structure is a subjective task, because it depends on the assumption that the criteria for recognition of their parts and their relationships. Therefore, the identification of a cognitive goal-oriented structure and is dependent on existing knowledge.
Oxygen is one of the existing dangerous addictive substances on earth. All of mankind is born addicted to substances, five minutes without inhaling these substances, humans will be hooked with the characteristics of gasping and eventually died. National Narcotics Agency in a press releasenya, has admitted defeat in this fight against the circulation of narcotic substances, because all of his staff already suffering from chronic addiction to oxygen.
Compiler basic cells of our body is, the dynamics of metabolism to keep the wheels work function of each organ we know as life, the main kitchen is a cell. To perform its functions of our body cells require a source of energy in a very large portion, which is supplied from 90% glucose (the smallest molecules from carbohydrate metabolism). Differences with carnivores who obtained 90% energy from oxidation of amino acids (the smallest molecule of protein). Only amino acid required by the WHO only in small amounts (2.5 to 4%) or only about 25 grams of unsaturated fatty acids (1 +%), vitamins, less than 1%.
Oxygen required for metabolism. Metabolism is the process of processing (formation and decomposition) substances that are needed by the body so the body can perform its functions.
In biology, the organism is any living system (such as animals, plants, fungi, or micro-organisms). At least in some form, all organisms capable of responding to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homeostasis as a whole is stable. An organism may be unicellular (single celled) or consist of, as in humans, many billions of cells grouped into specialized tissues and organs. The term multicellular (many celled) describes any organism consists of more than one cell.
Approximately twelve to 15 breaths per minute an adult needs - around 20,000 breaths a day. With every breath about half a liter of air inhaled. If physical activity can increase this number further. lungs with the heart and large blood vessels in the chest. It consists of two lungs, which in turn are divided into several lobes - two left, a little bigger right lung into three lobes. Space between the two lungs called the mediastinum. It also runs the trachea, blood vessels, lymph vessels and esophagus. Both the second surface of the lungs and chest cavity of the inner wall with the skin, lungs and pleura, covered.
lobe is the name of the species Latimeria coelancanth chalumnae.Ikan lung kolam.Ikan live in the swamp and the lungs will increase the surface to breathe.
Mediastinum is the cavity between the lungs that contains the right and left heart, aorta, and major arteries, major veins, trachea, thymus gland, nerves, connective tissue, lymph nodes and channels.
Mediastinal cavity is divided into four important:
1. Superior mediastinum, the chest cavity door began to torakal to-5 vertebra and the lower sternum
2. Anterior mediastinum, the superior mediastinal border line to the diaphragm in front of the heart
3. Posterior mediastinum, the mediastinal superiro boundary line to the diaphragm at the back of the heart
4. Medial mediastinum (center) from the line of the superior mediastinum to the diaphragm boundary between the anterior and posterior mediastinum.
The trachea is a tuba that has a diameter of 20-25 mm and a length of about 10-16 cm. Lies of the larynx and trachea terbifurkasi into the main bronchi in mammals, and from the pharynx to syring in birds, which is the entrance of air into the lungs.
Lymphatic vessels containing viscous fluid (lymph nodes), which consists of fat and fluid containing white blood cells. In addition to the lymph vessels there are specific areas, namely the lymph nodes, tonsils (tonsils, bone marrow, spleen, liver, lungs and intestines, where the lymphocytes can be loaded, transported and distributed to the parts that need it as part of the immune response. Plan which genius of this system ensures the availability and preparation of immune responses immediately, wherever necessary. Swollen lymph nodes occurs because the lymph vessels drain the infection by took him to the nearest area where the immune response can be executed.
When breathing, air flow through the nose or mouth into the trachea, which is divided into two main bronchi. Two main bronchi enter the lungs and then divides into branches that are smaller and smaller and more subtle - the bronchi and bronchioles. At the end of the smallest bronchioles sat a total of approximately 300 million alveoli, the alveoli, where there is a so-called "gas exchange". Through the walls of the alveoli, which is surrounded by a network of fine blood vessels, inhaled oxygen is absorbed into the blood and carbon dioxide as a waste product of metabolic processes, made from the blood into the lungs and sighed. Converted all alveoli exchange area around 160 square meters surface area, roughly the size volleyball court. This is far more than he needs to survive - so it can be a man
required by a living lung.
Bronchus is the liaison between the lungs with the trachea. Bronchial-pulmonary diparu have the right and left. Which is called bronchial branching bronchus.
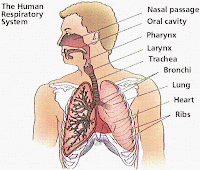
The road delivers breathing air into the lungs is the nose, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus principalis, bronchus lobaris, bronchus segmentalis, bronchial terminalis, respiratory bronchial, alveolar ductus, saccus alveolar, and alveoli.
The trachea is a tuba that has a diameter of 20-25 mm and a length of about 10 cm. The trachea is a hollow tube supported by rings of cartilage. Tracheal cartilage krikoid originated from the ring-shaped seal and extends to the anterior of the esophagus, down into the thoracic vertebrae to-five and beyond where it divides into two main bronchi (primary right and left) on Karina. Order form than 16-20 tracheal rings composed of hyaline prone incomplete, resembling the letter C. Incomplete letters section this leads to the posterior and filled in by smooth muscle. In place of tracheal branching, there is one angle between the left and right primary bronchus is identified as Karina. Tracheal epithelium coated by pseudostratum bersilium column. Trachea function is to provide a place for the air that was brought in and the air is expelled.
Trachea also is:
- Very flexible
- Muscular
Large blood vessels in the neck runs parallel to the trachea on the lateral and encased in the carotid sheath. Thyroid gland is located in the trachea in the front and laterally. Ismuth passing anterior to the trachea, usually as high as second to fifth tracheal ring. Recurrent laryngeal nerve lies in the tracheoesophageal groove. Beneath the subcutaneous tissue and trachea on the front cover is a supra-sternal muscles attached to the thyroid cartilage and hioid.





.jpg)


















